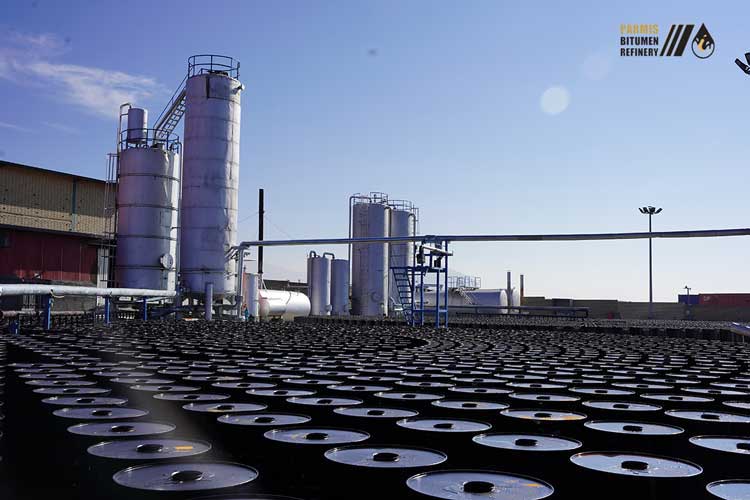
Bitumen is an important material in both large and small construction projects in Iran, and it contributes significantly to structural durability. Each type of bitumen, from 60/70 to 85/100, has unique characteristics, and selecting the right one can have a significant impact on project quality.
Bitumen prices fluctuate in the market, so keep this in mind when making a purchase. This article contains all of the necessary information in one place. For a more in-depth understanding and more confident decision-making, we recommend reading the entire Parmis website.
Types of Iranian Bitumen and their Technical Properties
Iran bitumen is important in many industries and is produced in a variety of forms. Each type has distinguishing characteristics that make it appropriate for specific applications. The following are the main types of bitumen produced in Iran:
Blown Bitumen (Oxidized Bitumen): This type is created during the final stages of refining by blowing hot air into the bitumen. It has greater flexibility than penetration-grade bitumen.
Cutback bitumen is created by combining bitumen with solvents like gasoline or kerosene. Because it remains liquid at room temperature, it is commonly used in road construction and surface treatment.
Emulsion Bitumen: This type is created by combining bitumen with water and emulsifiers. It is widely used in cold asphalt applications and rapid road maintenance because it is less flammable and easier to handle.

Blown Bitumen and Mechanical Properties
Blown bitumen is created in the final stages of the refining process. This method involves blowing hot air at temperatures ranging from 200 to 300°C into the bitumen tank. This process initiates a hydrogen-oxygen reaction, which produces water and leads to polymerization. As a result, the bitumen’s structure changes, becoming softer and more resistant to temperature fluctuations.
Technically, blown bitumen has lower penetration than penetration-grade bitumen. This makes it appropriate for environments with high temperature fluctuations. It is widely used to make waterproofing sheets, car batteries, and protective coatings. Because of its high heat resistance, it is also commonly used in tropical regions.
Cutback Bitumen and the RC/MC Classifications
Cutback bitumen is bitumen mixed with solvents like gasoline or kerosene. These solvents keep the bitumen liquid at room temperature, making it easier to apply. As a result, cutback bitumen is frequently used in road construction and surface coating applications.
Cutback bitumen is classified based on the evaporation rate.
- RC (Rapid-Curing): Made with light solvents such as gasoline, it evaporates quickly and is ideal for projects that require fast setting.
- MC (Medium-Curing): Made with heavier solvents, it evaporates slower and is ideal for moderate climates and long-term projects.
Emulsion Bitumen and the Function of Emulsifiers
Emulsion Bitumen is composed of bitumen, water, and emulsifying agents. Emulsifiers, such as alkaline salts or organic acids, charge bitumen droplets, preventing them from sticking together and suspending them as tiny particles in water.
The primary advantage of emulsion bitumen is that it reduces fire and environmental risk by eliminating the use of flammable solvents. It is quick to apply and ideal for cold asphalt, emergency repairs, and waterproofing.
Specialized applications of Iranian bitumen in various industries
Understanding the technical characteristics of each type of bitumen aids in the proper selection for industrial projects. Furthermore, comparing bitumen prices streamlines the purchasing process. The following are the key applications of bitumen in various industries:
Construction and Waterproofing: Prevents water infiltration on rooftops, bathrooms, and floors.
Road construction and asphalt production are necessary for hot and cold asphalt, crack sealing, and high-traffic road surfacing. In this category, viscosity grade bitumen performs best.
Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical Industries: Used to protect equipment, tanks, and facilities from moisture and chemicals.
Other Industries: Used in agriculture, coke production, and even as a fuel source in certain projects.
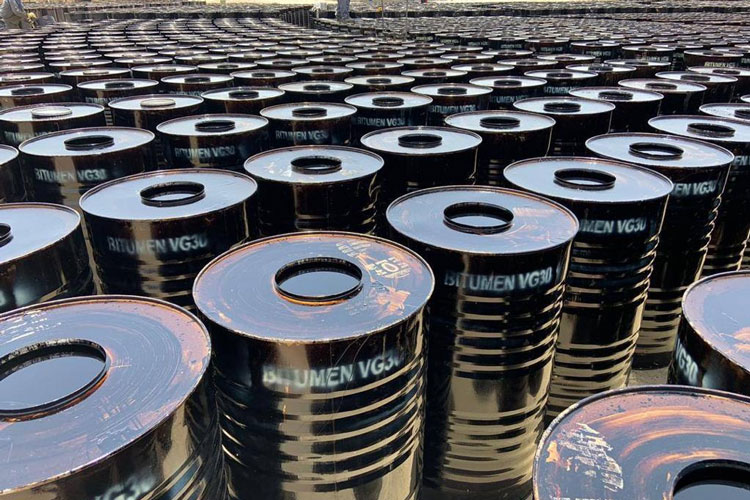

Standards and classification of construction bitumen in Iran
Construction bitumen in Iran is classified according to penetration grade and application conditions. Each category has distinct characteristics that are appropriate for different areas of a building.
For instance, the most widely used kind of roof waterproofing is Jey bitumen 60/70, which has medium penetration. Harder grades, on the other hand, like Pasargad bitumen 85/100, are utilized in hot climates or final layers.
Softening point, hardness, and moisture resistance are all considered when classifying materials. As a result, contractors must carefully select the appropriate type. Using the correct standard extends the life of a structure and lowers maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Iranian bitumen is important not only for domestic projects but also on a global scale. It is used in many industries, including petrochemicals, road construction, and building insulation. Each type—blown bitumen, cutback bitumen, and emulsion bitumen—has distinct characteristics that, when used correctly, improve project quality.
Construction standards emphasize the importance of accurate selection. In this article, we looked at the characteristics and applications of different types of bitumen, as well as how bitumen pricing and purchasing methods affect project outcomes. For more detailed information, please visit the Parmis website’s other educational resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common applications for 60/70 bitumen?
This grade is suited to moderate climates and is commonly used in road asphalt and building waterproofing.
What’s the difference between blown and penetration-grade bitumen?
Blown bitumen is tougher and more heat-resistant, making it ideal for roofing and protective coatings. Penetration-grade bitumen is softer and used primarily in asphalt production.
Why is selecting the right bitumen critical?
Choosing incorrectly can result in cracking or surface softening. Selecting the right bitumen increases durability and lowers maintenance costs.
What advantages does emulsion bitumen have over cutback bitumen?
Emulsion bitumen mixes with water and is safer to transport than cutback bitumen, which contains solvents and pollutes more.
Where is 85/100 bitumen best suited?
This softer grade is ideal for tropical regions. Its flexibility at high temperatures helps to keep asphalt from cracking.
Can we recycle old asphalt?
Yes. Old asphalt can be crushed and mixed with new bitumen, lowering costs and promoting environmental sustainability.